Uses of an OT Dress and Surgical Blades.
OT Dress:
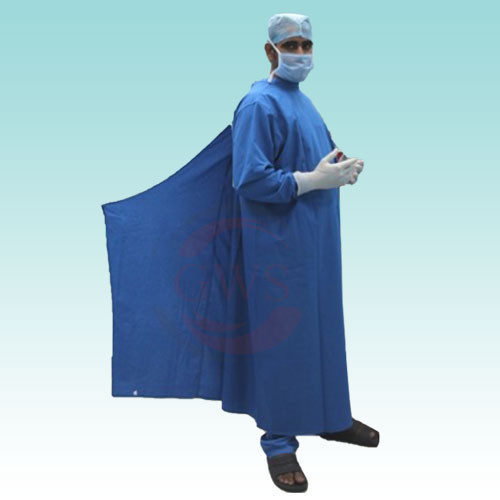
An Occupational therapy dress (OT dress) acts as a barrier between the patient and the surgical team. Its use prevents cross contamination and protects healthcare workers from bodily fluids. It also promotes sterility in the operating room, which prevents HAIs. Here are some of the other uses of an OT dress. Read on to learn more! How do you use an OT Dress? The benefits are extensive and include reducing the risk of infection and protecting healthcare workers.
Occupational therapy dresses are a barrier between the surgical team and the patient:
Occupational therapy (OT) staff typically wears protective surgical gowns and masks. These gowns and masks prevent shedding of hair and skin particles, and prevent contact with bodily fluids from the patient. As a barrier between the surgical team and the patient, OT scrub dresses are important to protect the healthcare team and minimize risk of microbial spread. Occupational therapy (OT) dresses are typically green or surgical blue in color.
Occupational therapy (OT) dresses are designed to restrict movement and prevent distraction. Most OT teams wear green or blue OT gowns, as other colors are distracting to the patient. Dresses made of sterile materials should also restrict movement for the surgical team. OT gowns and masks are available in many sizes and styles. Some have tactile sensitivity buttons or a velvet lining.
They protect healthcare workers from bodily fluids:
While healthcare providers are often exposed to bodily fluids, they must follow a series of precautions to prevent infection. These include hand hygiene, personal protective equipment (PPE) based on anticipated exposure, safe injection practices, and proper management of contaminated equipment and items in the patient’s environment. The principles of these precautions apply to all types of healthcare workers, whether they are providing direct care, assisting in surgery, or performing other medical procedures.
The American Red Cross recommends that health care workers use protective barriers to protect themselves from blood, bodily fluids, and other potentially infectious materials. These precautions are crucial for protecting patients and healthcare workers from infection. Depending on the profession, they may include gloves, gowns, masks, eye protection, and other equipment. If no blood is present, it’s wise to wear protective barriers, including face masks and eye protection.
They promote sterility in the operating room:
Some methods of sterility promotion have been proven to be effective, but they cannot completely eliminate bioburden. A patient and an employee’s breath aerosols can introduce host-associated microbes into the operating room, despite best efforts. Various attempts have been made to minimize the bioburden, such as the use of protective suits and hoods for health personnel and surgical instruments. However, some surgical procedures are inherently riskier and require a full sterile operating room.
Sterile field principles are essential in preventing a surgical site infection (SSI), a common and preventable infection after surgery. Sterile techniques are essential in preventing SSIs, which occur when bacteria or other microbes enter the surgical site. They include wearing gloves and gowns, observing for broken techniques, and using only sterile materials. Listed below are several common sterile technique principles:
They prevent HAIs:
The top priority for infection prevention is zero HAIs, but how can you prevent them? Infection control policies, hand hygiene, and antibiotic stewardship can all make a difference. Hospitals should set their own goals and establish a committee to address infection prevention and control. The committee should decide on evidence-based practices and written guidelines, as well as the culture that will be fostered in order to stop HAIs.
Hospitals can use measures to measure progress and determine if any changes are effective. Examples include the rate of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus per 1,000 patient days or the percent of patients with Clostridium difficile associated disease. Other measures to consider include hospital cleanliness and hand hygiene compliance. However, many hospitals fail to achieve zero HAIs. They should strive to prevent infection risks and maximize patient satisfaction.
The Many Uses of a Surgical Blade:
There are various uses of a Surgical Blade. Here are some of the most common types and their various uses. The number 10 blade is used for small cuts in muscle or skin. It can also be used for making distal arteriotomy in cardiac surgery. This blade is sharp and can make incisions evenly. The number 22 blade is bigger and can be used for large incisions in thick skin. This surgical blade is sharp and has a flat back edge. It can be easily handled because it does not bend easily.
Surgical blades are used in many different types of surgeries. They are a critical part of the operating room and need to be sharp to cut human tissue and skin. In addition to blades, operation rooms have other tools, including surgical lightings and other equipment. Surgical Blade manufacturers in Italy are specialized in developing good quality blades. They have extensive experience and theoretical knowledge in the industry. These tools help physicians perform surgery safely and quickly.
The curved blade has a blunt back portion and a sharp front edge. It is used for incisions and drainage. It can also be used for puncturing sebaceous glands and lipomas. Surgical blades with rounded tips are often used for delicate procedures in the hand and foot. They are ideal for debridement and the removal of soft corns. The sharp hooked front end of a Surgical Blade can be used to separate thick tissue and nonvascular membranes.